 Audio file formats are digital file types that contain audio data. They are used to store and transmit audio recordings; each format has unique features and characteristics. Audio file formats can be categorized into three types: lossy, lossless and uncompressed. Lossy file formats use compression to reduce the file size by eliminating some audio data, resulting in some quality loss. In contrast, lossless file formats compress the file size while preserving all the audio data, resulting in no quality loss. Uncompressed file formats do not use compression and retain all the audio data, resulting in large file sizes.
Audio file formats are digital file types that contain audio data. They are used to store and transmit audio recordings; each format has unique features and characteristics. Audio file formats can be categorized into three types: lossy, lossless and uncompressed. Lossy file formats use compression to reduce the file size by eliminating some audio data, resulting in some quality loss. In contrast, lossless file formats compress the file size while preserving all the audio data, resulting in no quality loss. Uncompressed file formats do not use compression and retain all the audio data, resulting in large file sizes.
Converting audio file formats is essential in many situations, such as when trying to play a file on a device that's incompatible with its format or when trying to reduce the file size. For example, some music players and smartphones only support specific audio file formats; if a file is not in the required format, it won't play. Similarly, if the file size is too large, it may take up too much storage space or be difficult to transmit over the internet. Converting an audio file to a different format can solve these issues.
Click here to try our free online Audio File Converter.
This article will cover everything you need to know about converting audio file formats. We'll start by explaining the different types of audio file formats, including lossy, lossless and uncompressed. Then, we'll discuss the factors to consider before converting an audio file format, such as the purpose of conversion, quality loss, compatibility with devices and software, file size and time and resources needed for conversion. Next, we'll explain the various tools available for converting audio file formats, including online converters, desktop software and mobile apps. We'll then provide step-by-step instructions on converting an audio file, as well as tips for success and troubleshooting common issues. Finally, we'll emphasize the importance of choosing the appropriate audio file format and provide final thoughts and recommendations. By the end of the article, you'll have all the information you need to convert audio file formats efficiently and effectively.
Understanding the different types of audio file formats is essential when converting them. It's critical to consider the purpose of conversion, compatibility with devices and software and the desired audio quality before selecting a file format. Each file format type has unique characteristics and features, making it suitable for specific applications. By choosing the appropriate file format, you can ensure that your audio recordings are of the highest quality and can be played on most devices and platforms.
Lossy file formats are compressed file types that use algorithms to reduce the file size while eliminating some audio data, resulting in some quality loss. Lossy file formats are the most commonly used audio file formats because of their small file sizes and widespread compatibility with devices and software. Here are some of the most popular lossy file formats:
 MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3) is one of the most popular and widely used audio file formats. It uses a compression algorithm that can reduce the file size by up to 90% while preserving most of the audio quality. MP3 files are compatible with most devices and software and can be played on many platforms, from music players to smartphones.
MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3) is one of the most popular and widely used audio file formats. It uses a compression algorithm that can reduce the file size by up to 90% while preserving most of the audio quality. MP3 files are compatible with most devices and software and can be played on many platforms, from music players to smartphones.Lossless file formats are compressed file types that retain all the audio data without any quality loss. Lossless file formats are preferred by audiophiles and music producers who require high-quality audio recordings. Here are some of the most popular lossless file formats:
Uncompressed file formats are digital file types that retain all the audio data without compression. Uncompressed file formats are used for high-quality audio recordings and mastering. Here are some of the most popular uncompressed file formats:
Audio file conversion is a crucial process that requires proper planning and consideration to ensure that the output file format meets your needs. Before converting an audio file from one format to another, you need to consider the purpose, quality loss, compatibility, file size and available time and resources to avoid any unexpected outcomes. Considering these factors, you can choose the appropriate output file format that best suits your needs and ensures high-quality sound.
 Before you convert an audio file, you should first establish the purpose of the conversion. Are you looking to save space, improve quality, or enhance compatibility with specific devices or software? Understanding the purpose of the conversion will help you determine the output file format that best suits your needs.
Before you convert an audio file, you should first establish the purpose of the conversion. Are you looking to save space, improve quality, or enhance compatibility with specific devices or software? Understanding the purpose of the conversion will help you determine the output file format that best suits your needs.
For instance, if you want to reduce the size of an audio file for ease of sharing or storage purposes, you may opt for a lossy file format such as MP3 or AAC. On the other hand, if you want to maintain high-quality sound, you may choose a lossless format such as FLAC or ALAC. Therefore, the purpose of the conversion is a crucial factor in determining the output file format.
Another factor to consider when converting audio file formats is quality loss. Converting an audio file from one format to another can result in a loss of quality, especially when converting from a lossless to a lossy file format. The extent of quality loss depends on the specific file formats and the quality settings used during the conversion process.
To minimize quality loss, it's advisable to use the highest quality settings possible during the conversion process. However, remember that higher-quality settings result in larger file sizes, which may impact storage space and compatibility with specific devices and software.
Compatibility is another critical factor to consider when converting audio file formats. You should ensure that the output file format is compatible with the devices or software you intend to use to play or edit the audio file. For instance, if you want to play an audio file on an Apple device, you may need to convert it to a format compatible with the device's default media player.
Before converting an audio file, research the file formats compatible with your devices and software and choose the appropriate format to avoid any compatibility issues.
File size and storage space are other important factors when converting audio file formats. Lossless file formats such as FLAC and ALAC produce high-quality audio but result in large file sizes. On the other hand, lossy file formats such as MP3 and AAC make smaller file sizes but with lower quality.
Therefore, you should consider the available storage space on your device or storage medium before deciding on the output file format. You may opt for a lossy format to save space if you have limited storage space. However, if storage space is not an issue, you can choose a lossless format for better sound quality.
Converting audio file formats can be a time-consuming process, depending on the file size and the speed of your computer or device. Before starting the conversion process, ensure you have enough time and resources to complete the process.
For instance, converting a large audio file from a lossless format to a lossy format can take a long time, especially if you use low-quality settings. Therefore, plan accordingly and allocate enough time and resources to ensure a successful conversion.
Converting audio file formats is an essential task for many people; luckily, several tools are available for this purpose. The type of tool that you choose depends on several factors, such as your skill level, the number of files you need to convert and the formats you want to convert to. Make sure you choose a tool that's easy to use and supports the audio file format you need to convert. This section will explore some of the most popular tools for converting audio file formats.
Online converters are web-based tools that allow you to convert audio files without installing any software on your computer. These tools are ideal for people who need to convert audio files occasionally and do not want to download and install any software. They are easy to use, and most support a wide range of audio file formats.
 Desktop software is another popular tool for converting audio file formats. This software is installed on your computer and allows you to convert audio files in batches. One of the most popular desktop software for converting audio files is iTunes, which is available for both Mac and Windows. Other desktop software options include Audacity, Switch and Freemake Audio Converter. Desktop software is ideal for people with many audio files that need to be converted.
Desktop software is another popular tool for converting audio file formats. This software is installed on your computer and allows you to convert audio files in batches. One of the most popular desktop software for converting audio files is iTunes, which is available for both Mac and Windows. Other desktop software options include Audacity, Switch and Freemake Audio Converter. Desktop software is ideal for people with many audio files that need to be converted.
Mobile apps are becoming increasingly popular for converting audio file formats. These apps are available for iOS and Android devices and can be downloaded from the app store. Some popular mobile apps for converting audio files include Audio Converter, File Converter and Media Converter. Mobile apps are ideal for people who want to convert audio files on the go and do not have access to a computer.
Converting audio file formats can seem daunting, but the process can be pretty simple if you follow the proper steps. Here are the basic steps to convert an audio file:
Before converting an audio file, you need to select the file you want to convert. This can be a file stored on your computer, an external hard drive, or even a CD or DVD.
The next step is to choose the output format. This will depend on what you plan to do with the file after it has been converted. For example, if you want to play the file on an iPod, you may want to choose the MP3 format. If you want to preserve the highest possible quality, you may want to choose a lossless format like FLAC or ALAC.
After you have chosen the output format, you may want to adjust some settings and parameters. For example, you may want to change the bitrate or sample rate to get a specific level of audio quality or file size. Remember that adjusting these settings can impact the audio quality and file size.
Once you have chosen the file and output format and adjusted any necessary settings, it's time to convert the file. The exact steps will depend on the tool you are using. Online converters and mobile apps typically have a simple "convert" button, while desktop software may have more options.
Finally, you need to save the converted file once the conversion process is complete. Be sure to save the file in a location where you can easily find it later. You may also want to double-check that the file can be played on the intended device or software.
With these basic steps, you can easily convert audio file formats and ensure that your music, podcasts and other audio files are playable on any device or software. Remember that the specific steps and options may vary depending on the tool you are using, but the basic principles remain the same.
 The ability to convert audio file formats can be helpful in many situations, but it's essential to ensure that the process is done correctly. Factors such as the purpose of the conversion, device and software compatibility, and original file quality all affect the final result. Here are some tips to keep in mind to help ensure a successful audio file conversion. By following these tips, you can be confident that your audio file conversion will succeed.
The ability to convert audio file formats can be helpful in many situations, but it's essential to ensure that the process is done correctly. Factors such as the purpose of the conversion, device and software compatibility, and original file quality all affect the final result. Here are some tips to keep in mind to help ensure a successful audio file conversion. By following these tips, you can be confident that your audio file conversion will succeed.
Before starting the conversion process, it's always a good idea to keep a backup copy of the original audio file. This can come in handy if something goes wrong during the conversion process or if the converted file doesn't meet expectations.
The quality of the original audio file can impact the quality of the converted file. So, it's always a good idea to use high-quality sources to ensure the best possible outcome. It's worth noting that some audio file formats, like MP3, are already compressed, so converting them to another format may result in a loss of quality.
It's essential to consider the purpose of the converted file when choosing the output format. For instance, if the file is intended for use on a mobile device, a lossy format like MP3 may be appropriate due to its smaller size. However, a lossless format like FLAC may be more appropriate if the file is intended for professional use.
It's essential to consider the device and software used to play the converted file. For example, if the file is intended for an Apple device, it may be best to choose a format like AAC that's optimized for Apple products. It's also worth noting that some software may not support specific file formats.
Once the conversion process is complete, it's essential to check the quality of the converted file. This can be done by listening to the file and comparing it to the original or using software tools to analyze the file's technical details like bit rate and sample rate. If the quality is not up to par, it may be necessary to try converting the file again with different settings or software.
Audio file conversion can sometimes lead to issues such as incomplete or failed conversions, poor audio quality, incorrect output formats, device or software compatibility issues and other problems. Here are some tips for resolving common issues that may arise during the audio conversion process.
Incomplete or failed conversions can occur due to a variety of reasons. One common cause is a lack of sufficient disk space, which can prevent the converted file from being saved. Another cause could be a corrupt source file or an issue with the converter software. In such cases, trying to convert the file using a different tool or to repair the source file is recommended.
Poor audio quality after conversion can result from a low bitrate setting or a lossy format like MP3 or AAC. It's recommended to use high-quality source files and to select a lossless format like FLAC or ALAC to prevent significant loss of audio quality. It's also essential to adjust the bitrate and sample rate settings to achieve the desired balance between file size and audio quality.
Incorrect output format can occur when the target device or software does not support the chosen output format. To avoid this issue, it's essential to understand the target device or software's requirements before choosing an output format. If unsure, it's advisable to consult the device or software manual or online support resources to determine the appropriate format to use.
Device or software compatibility issues can occur when the converted file doesn't play on the target device or software. This can happen when the target device or software doesn't support the chosen output format or when the file's settings, such as bitrate or sample rate, are incompatible with the target device or software. It's recommended to check the target device or software's specifications and requirements before choosing the output format and adjusting the file settings.
To avoid common audio conversion issues, it's essential to use high-quality source files, choose the appropriate output format, adjust the bitrate and sample rate settings and ensure compatibility with the target device or software. It's also recommended to keep the original file for backup purposes in case of errors during the conversion process. If any issues arise, it's advisable to consult the device or software manual or online support resources or to try converting the file using a different tool. Additionally, it's essentialto check the quality of the converted file before using it to ensure that it meets the desired standards.
In conclusion, converting audio file formats can be necessary to ensure compatibility, reduce file size and optimize sound quality. In this article, we've explored the different types of audio file formats, the factors to consider before converting, the tools and steps involved in the conversion process, and tips and troubleshooting solutions to ensure the best possible results.
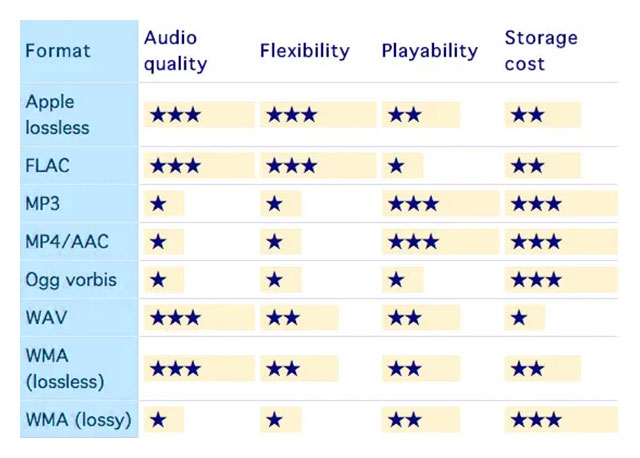
When choosing the appropriate audio file format, it's essential to consider the purpose of the file and the playback device or software that will be used. Lossy formats like MP3 or AAC are an excellent option for streaming and mobile devices, while lossless formats like FLAC or ALAC are ideal for audiophiles who value high-fidelity sound. Uncompressed formats like WAV, AIFF or DSD are suitable for professional recording and mastering purposes.
Regardless of the format chosen, it's essential to use high-quality sources and check the converted file's quality to ensure it meets the desired specifications. Following the steps and tips outlined in this article, you can convert your audio files confidently and achieve the best possible results.
Overall, converting audio file formats can be a complex and technical process, but with the right tools and knowledge, it can be done effectively and efficiently. Always take the time to consider the purpose of the file, the compatibility with your playback device and software and the quality of the source material to ensure the best possible results.